
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) conducted its monetary policy meeting from February 5-7, 2025.
On the basis of an assessment of the evolving macroeconomic situation, the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) made the following announcements:
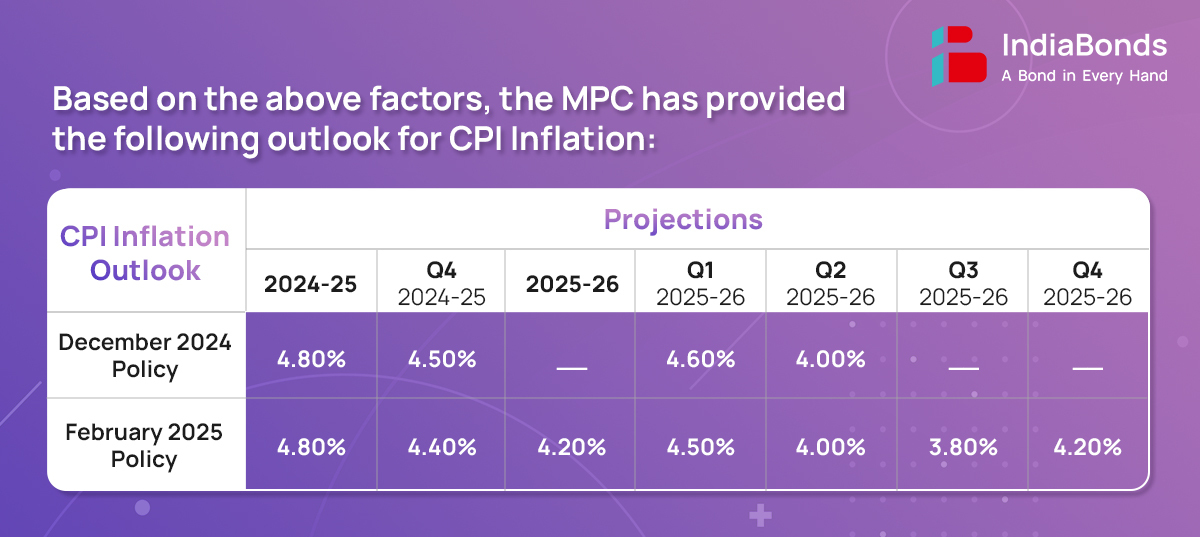
CPI Headline inflation eased sequentially in Nov’24 and Dec’24 from its recent peak of 6.2% in Oct’24. The decline was primarily driven by a moderation in food inflation, as vegetable price inflation retreated from its Oct’24 high. Core inflation remained subdued across both goods and services, while the fuel continued to experience deflation.
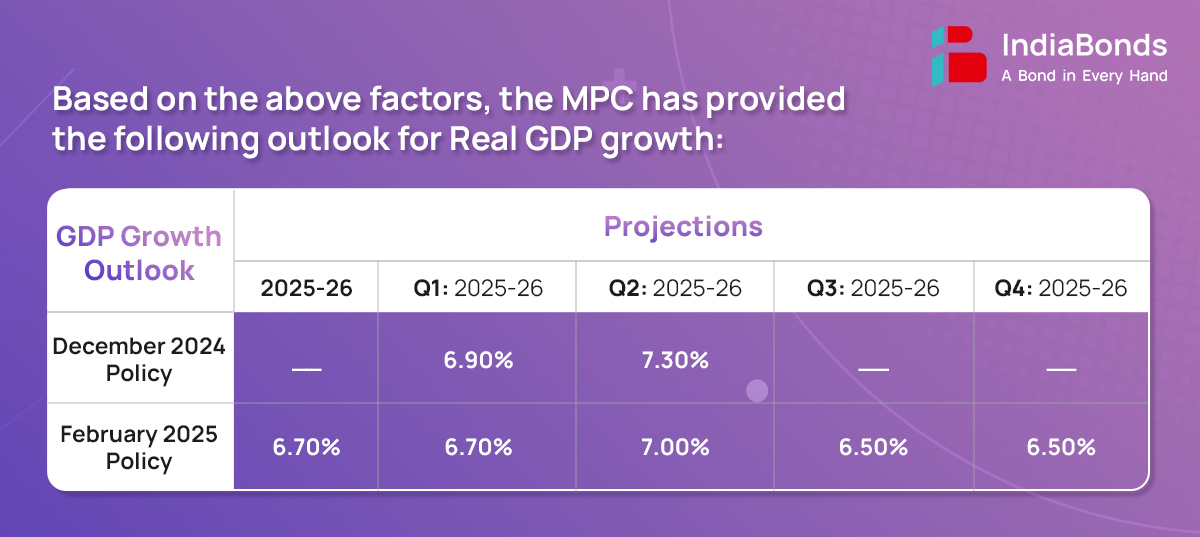
As per the first advance estimates, real GDP growth for FY25 is estimated at 6.4%, a softer expansion after a robust 8.2% growth in FY24. Agricultural activity remains upbeat on the back of healthy reservoir levels and bright Rabi prospects. On the demand side, rural demand continues to be on an uptrend, while urban consumption remains subdued with high frequency indicators providing mixed signals. Going forward, improving employment conditions tax relief in the Union Budget, and moderating inflation, together with healthy agricultural activity bode well for household consumption.
The global economy remains challenging, with growth below historical averages despite trade expansion. Global disinflation progress is stalling due to services price inflation. Reduced expectations of U.S. rate cuts have strengthened the dollar, increasing bond yields and triggering capital outflows from EMEs, causing currency depreciation and tighter financial conditions. India remains resilient but faces depreciation pressures. The RBI continues to deploy all available tools to navigate these challenges.
The MPC’s decision to lower the Repo Rate by 25 bps was in line with market expectations. However, the RBI’s action on the liquidity front did not align with market sentiments, as they were expecting some form of a CRR cut, liquidity injection or a change in stance to “accommodative.” This pushed the yield on the 10-year benchmark to around 6.70% post-policy, compared to the opening level of 6.64%. However, we believe, the risk to liquidity is currently emanating from RBI’s rupee management operations and could normalize whenever the rupee stabilizes. Hence, OMOs as per requirement would suffice instead of a durable CRR cut.
During the policy, the RBI noted that risks emerging to the domestic growth and inflation outlook from domestic factors remain limited but external factors could affect growth. RBI noted that the geopolitical tensions and protectionist trade policies continue to weigh on financial stability and domestic macro- dynamics, warranting a cautious approach going forward. Projections of growth as well as inflation have been revised slightly downwards.
Considering the current domestic macro dynamics and the volatility surrounding the exchange rate, we expect the RBI, in its April policy, to keep rates unchanged. However, there may be a shift in liquidity stance to “accommodative” from “neutral.
The RBI has undertaken various measures to enhance digital security in response to rising cyber threats and digital risks. These measures include Additional Factor of Authentication for domestic digital payments and even proposing to extend it to online international digital payments.
The RBI will also implement the exclusive ‘bank.in’ internet domain for Indian banks and ‘fin.in’ domain for the financial sector to help prevent banking frauds.
The RBI will include forward contracts in Government securities, enabling long-term investors, such as insurance funds, to manage their interest rate risks across interest rate cycles. Furthermore, it will enable efficient pricing of derivatives that use Government securities as underlying instruments.
To improve individual investors’ access to government securities, the RBI to extend the access of NDS-OM, a electronic trading platform for secondary market transactions in government securities, to non-bank brokers registered with SEBI.
The RBI will form a working group representing various stakeholders to undertake a comprehensive review of trading and settlement timings across various market segments. The group will submit its report by April 30th of this year.
The next meeting of the MPC is scheduled during April 7 to 9, 2025.
DISCLAIMER:
Disclaimer: Investments in debt securities/ municipal debt securities/ securitized debt instruments are subject to risks including delay and/ or default in payment. Read all the offer related documents carefully.